Nellore Fm
Type Locality and Naming
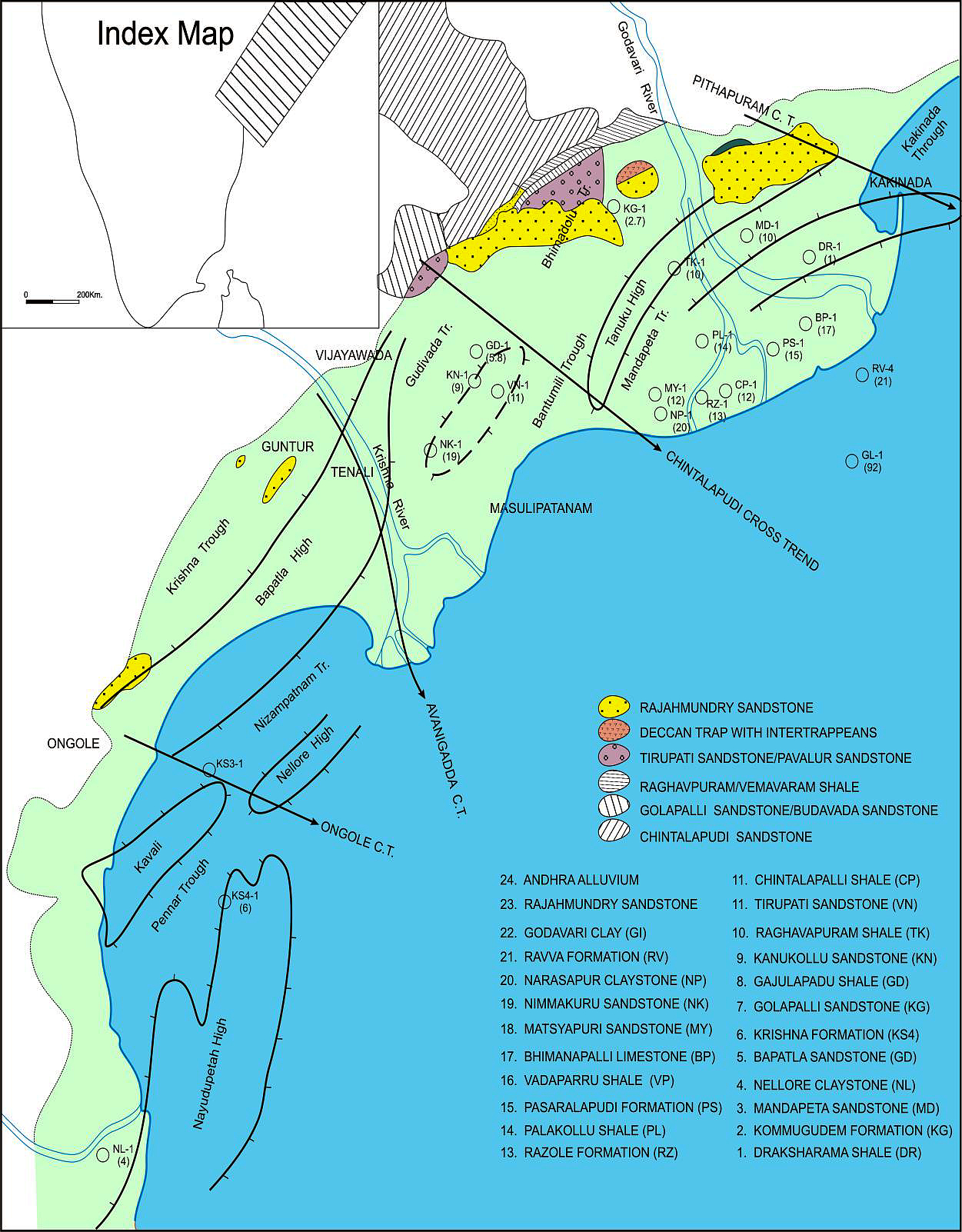
BASINAL: Named after Nellore town in Andhra Pradesh. The type section is located at exploratory well Nellore-A (depth interval: 2590-2960 m), in the Pennar graben. The hypostratotype is in the well KS-D-A (depth interval: 2120-2380 m). It was named after the Nellore town by ONGC team steered by Venkatarengan et al. (1993) and issued as Document-VII by KDMIPE, ONGC, Dehradun (1993). [Original Publication: Venkatarengan, R., Rao, G.N., Prabhakar, K.N., Singh, D.N., Awasthi, A.K., Reddy, P.K. and Palakshi, K. (1993) Lithostratigraphy of Petroliferous Basins, Document VIII, Krishna-Godavari Basin, KDMIPE, ONGC Publication, pp.1-29.]. Reference well: Kesanapalli – A (KS-D-A), Interval 2120-2380 m(?) and thickness 260 m (?).
Synonyms: Nellore Claystone
[Figure: Map showing the locations of designated holostratotype section for the formation in the KG Basin (After ONGC, Pandey and Dave, 1998) in Raju et al., 2021, ONGC Bulletin, Special Issue, Vol. 56, No. 2]
Lithology and Thickness
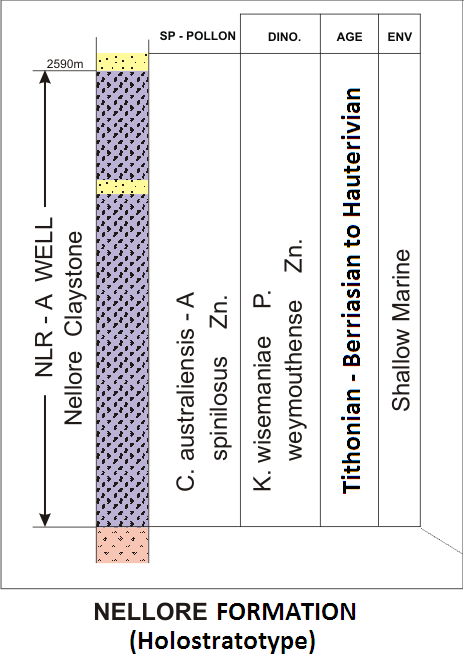
Sandy claystone. It is dominantly argillaceous with coarse-grained sandstones. The claystone is reddish-brown, chocolate brown, hard, micaceous and ferruginous. The sandstones are angular to sub angular, quartzite and poorly sorted with siliceous cement. The upper part of the section is sand. In the reference section, the lithology comprises of shale with minor sandstones. The shales are grey to dark grey, hard, micaceous, silty, and rarely carbonaceous. The sandstone is dirty white to grey very, fine to medium grained, subangular to subrounded, fairly well sorted, well cemented and calcareous. Its thickness varies from 300-370 m.
[Figure: Lithology, spore-pollen and dinoflagellate datums, age and environment of the holostratotype of the Nellore Formation in the Well NLR-A (after Bijai Prasad,1999)]
Relationships and Distribution
Lower contact
Unconformable with the Basement.
Upper contact
Conformable with the Krishna Fm.
Regional extent
Extends in Pennar and Nizampatnam grabens. Partly coeval with the Bapatla Fm sandstone.
GeoJSON
Fossils
Palynofossils of C. australiensis-A.spinolosus zone; Dinoflagellates of K. wisemaniae-P.waymouthense zone.
Age
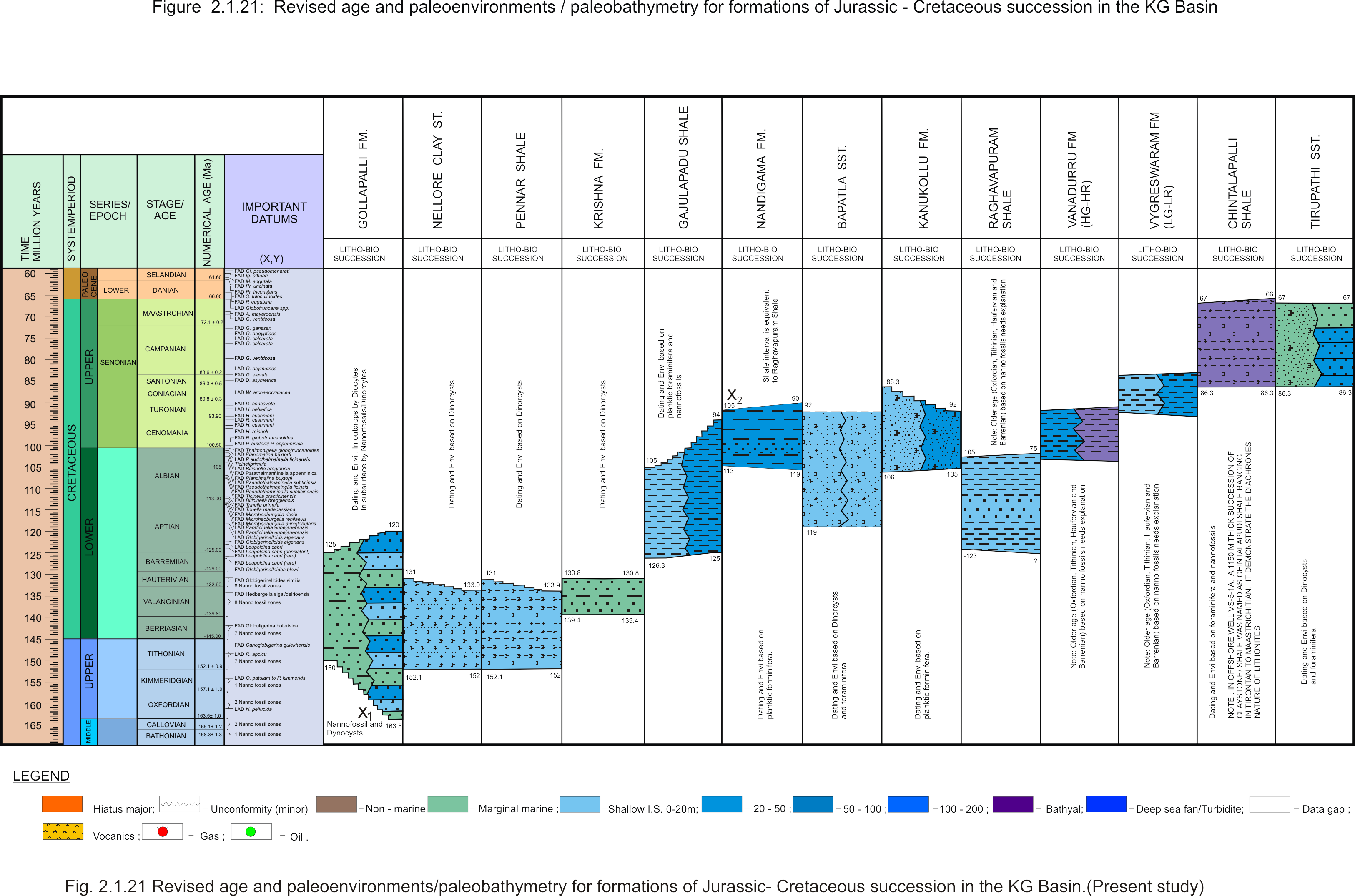
Depositional setting
Fluvial-Marginal marine.
[Figure: Revised age and paleoenvironments/paleobathymetry of formations of Jurassic-Cretaceous succession in KG Basin in Raju et al., 2021, ONGC Bulletin, Special Issue, Vol. 56, No. 2]
Additional Information